Page 11 - SGG_220316_Teachers_Handbook_Module_6
P. 11
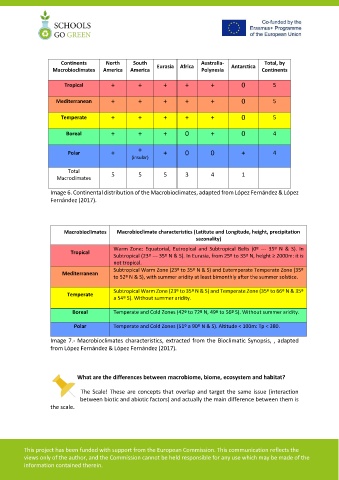
Continents North South Australia- Total, by
Macrobioclimates America America Eurasia Africa Polynesia Antarctica Continents
Tropical + + + + + 0 5
Mediterranean + + + + + 0 5
Temperate + + + + + 0 5
Boreal + + + 0 + 0 4
Polar + + + 0 0 + 4
(insular)
Total 5 5 5 3 4 1
Macroclimates
Image 6. Continental distribution of the Macrobioclimates, adapted from López Fernández & López
Fernández (2017).
Macrobioclimates Macrobioclimate characteristics (Latitute and Longitude, height, precipitation
sazonality)
Warm Zone: Equatorial, Eutropical and Subtropical Belts (0º - 35º N & S). In
Tropical
Subtropical (23º - 35º N & S). In Eurasia, from 25º to 35º N, height ≥ 2000m: it is
not tropical.
Subtropical Warm Zone (23º to 35º N & S) and Eutemperate Temperate Zone (35º
Mediterranean
to 52º N & S), with summer aridity at least bimonthly after the summer solstice.
Subtropical Warm Zone (23º to 35º N & S) and Temperate Zone (35º to 66º N & 35º
Temperate
a 54º S). Without summer aridity.
Boreal Temperate and Cold Zones (42º to 72º N, 49º to 56º S). Without summer aridity.
Polar Temperate and Cold Zones (51º a 90º N & S). Altitude < 100m: Tp < 380.
Image 7.- Macrobioclimates characteristics, extracted from the Bioclimatic Synopsis, , adapted
from López Fernández & López Fernández (2017).
What are the differences between macrobiome, biome, ecosystem and habitat?
The Scale! These are concepts that overlap and target the same issue (interaction
between biotic and abiotic factors) and actually the main difference between them is
the scale.
This project has been funded with support from the European Commission. This communication reflects the
views only of the author, and the Commission cannot be held responsible for any use which may be made of the
information contained therein.