Page 19 - SGG_220316_Teachers_Handbook_Module_6
P. 19
2.2. Global economy negative impacts on natural environment
It is common sense that nature and biodiversity Human driven negative impacts on natural
environment and biodiversity can be grouped in 5 major causes:
Habitat loss and fragmentation
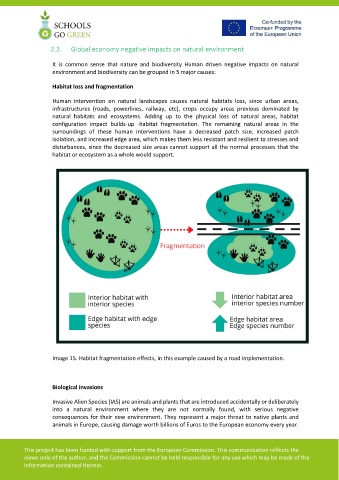
Human intervention on natural landscapes causes natural habitats loss, since urban areas,
infrastructures (roads, powerlines, railway, etc), crops occupy areas previous dominated by
natural habitats and ecosystems. Adding up to the physical loss of natural areas, habitat
configuration impact builds-up -habitat fragmentation. The remaining natural areas in the
surroundings of these human interventions have a decreased patch size, increased patch
isolation, and increased edge area, which makes them less resistant and resilient to stresses and
disturbances, since the decreased size areas cannot support all the normal processes that the
habitat or ecosystem as a whole would support.
Image 15. Habitat fragmentation effects, in this example caused by a road implementation.
Biological invasions
Invasive Alien Species (IAS) are animals and plants that are introduced accidentally or deliberately
into a natural environment where they are not normally found, with serious negative
consequences for their new environment. They represent a major threat to native plants and
animals in Europe, causing damage worth billions of Euros to the European economy every year.
This project has been funded with support from the European Commission. This communication reflects the
views only of the author, and the Commission cannot be held responsible for any use which may be made of the
information contained therein.